Future plans
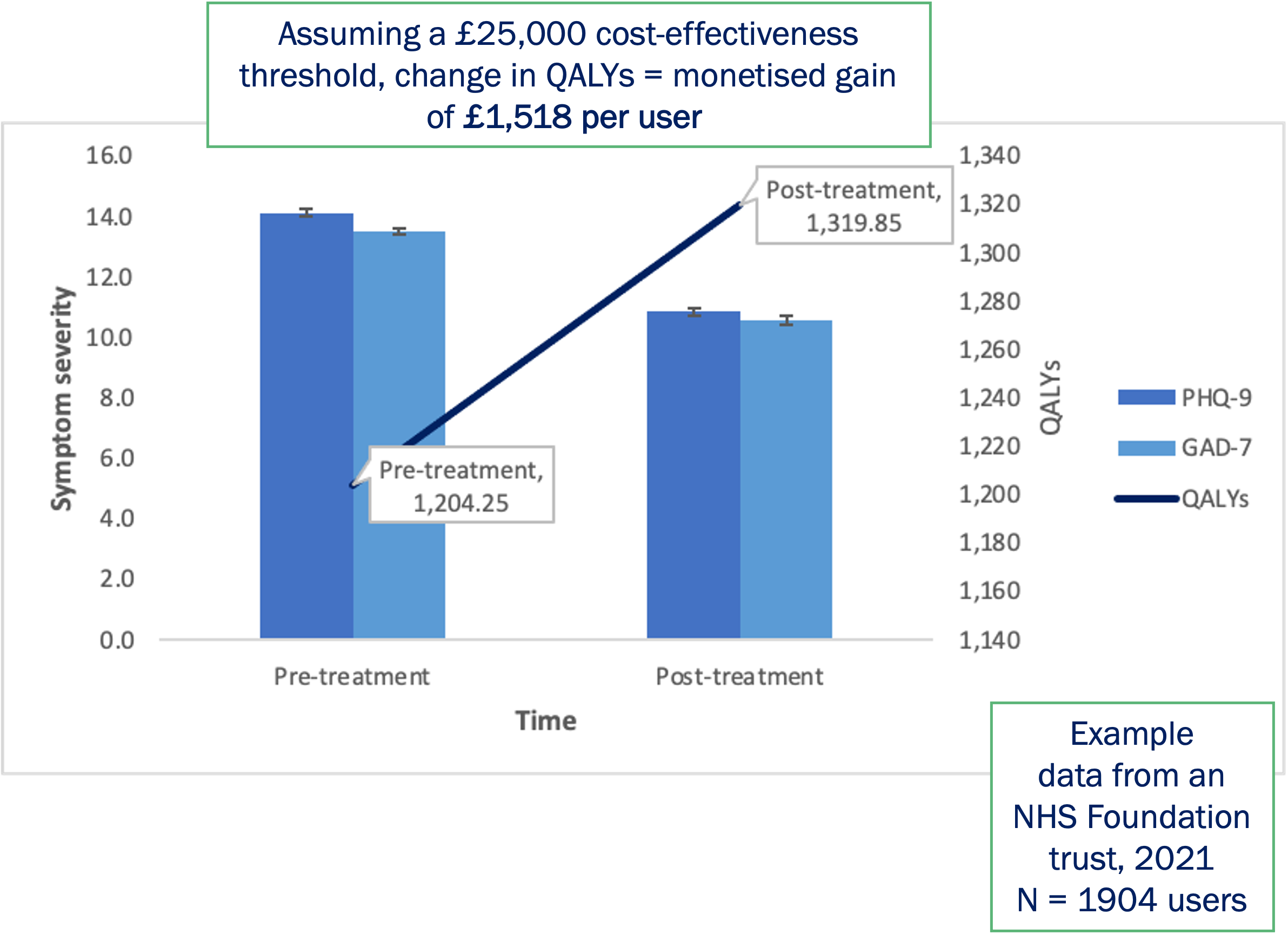
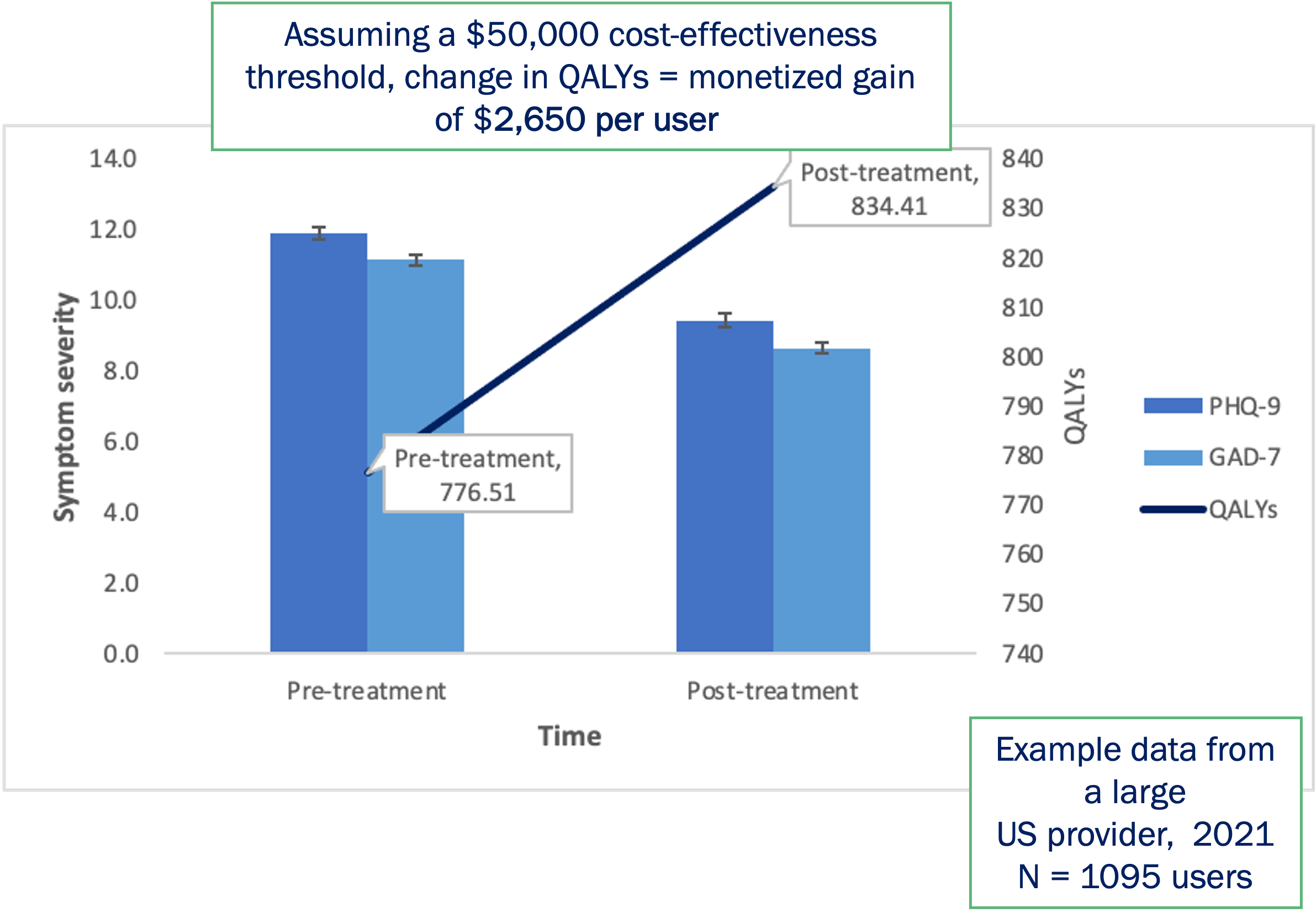
Amwell® will continue to use this mapping function to work with customers to understand the QALYs generated for their populations and the scale of economic impacts achieved. Further, future efforts will be undertaken to determine the relationships between QALYs and additional metrics, such as medical costs, within treated populations in order to understand the impact of cost-effective mental health treatment not only on the life of the individual, but the potential broader healthcare cost savings associated with improved mental wellbeing.
References:
Bestsennyy, O., Gilbert, G., Harris, A., & Rost, J. (2021). Telehealth: a quarter-trillion-dollar post-COVID-19 reality. McKinsey & Company.
Donker, T., Blankers, M., Hedman, E., Ljotsson, B., Petrie, K., Christensen, H., Ljótsson, B., Petrie, K., & Christensen, H. (2015). Economic evaluations of Internet interventions for mental health: a systematic review. Psychological Medicine, 45(16), 3357–3376. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291715001427
Franklin, M., & Alava Hernández , M. (2022). Enabling QALY estimation in mental health trials and care settings: mapping from the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 to the ReQoL-UI or EQ-5D-5L UK and US utility scores using mixture models. Paper Draft in Progress.
Keetharuth, A. D., Brazier, J., Connell, J., Bjorner, J. B., Carlton, J., Taylor Buck, E., Ricketts, T., McKendrick, K., Browne, J., Croudace, T., & Barkham, M. (2018). Recovering Quality of Life (ReQoL): a new generic self-reported outcome measure for use with people experiencing mental health difficulties. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 212(1), 42–49. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2017.10
ICER. (2015). Institute for Clinical and Economic Review: Integrating Behavioral Health into Primary Care: A Technology Assessment. http://icerorg.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/BHI_Final_Report_0602151.pdf
ICER. (2022). Institute for Clinical and Economic Review: 2020-2023 Value Assessment Framework. https://icer.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/ICER_2020_2023_VAF_02032022.pdf
Massoudi, B., Holvast, F., Bockting, C. L. H., Burger, H., & Blanker, M. H. (2019). The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of e-health interventions for depression and anxiety in primary care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 245, 728–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.11.050
Moshe, I., Terhorst, Y., Philippi, P., Domhardt, M., Cuijpers, P., Cristea, I., Pulkki-Råback, L., Baumeister, H., & Sander, L. B. (2021). Digital Interventions for the Treatment of Depression: A Meta-Analytic Review. In Psychological Bulletin (Vol. 147, Issue 8). https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000334
NICE. (2022a). Evidence standards framework for digital health technologies. https://www.nice.org.uk/about/what-we-do/our-programmes/evidence-standards-framework-for-digital-health-technologies
NICE. (2022b). Depression in adults: [B] Treatment of a new episode of depression. NICE guideline NG222 https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng222/evidence/b-treatment-of-a-new-episode-of-depression-pdf-11131004415
Paganini, S., Teigelkötter, W., Buntrock, C., & Baumeister, H. (2018). Economic evaluations of internet- and mobile-based interventions for the treatment and prevention of depression: A systematic review. Journal of Affective Disorders, 225, 733–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.07.018
Pauley, D., Cuijpers, P., Papola, D., Miguel, C., & Karyotaki, E. (2021). Two decades of digital interventions for anxiety disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment effectiveness. Psychological Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291721001999
Richards, D., Duffy, D., Blackburn, B., Earley, C., Enrique, A., Palacios, J., ... & Timulak, L. (2018). Digital IAPT: the effectiveness & cost-effectiveness of internet-delivered interventions for depression and anxiety disorders in the Improving Access to Psychological Therapies programme: study protocol for a randomised control trial. BMC psychiatry, 18(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186%2Fs12888-018-1639-5
Santomauro, D. F., Mantilla Herrera, A. M., Shadid, J., Zheng, P., Ashbaugh, C., Pigott, D. M., Abbafati, C., Adolph, C., Amlag, J. O., Aravkin, A. Y., Bang-Jensen, B. L., Bertolacci, G. J., Bloom, S. S., Castellano, R., Castro, E., Chakrabarti, S., Chattopadhyay, J., Cogen, R. M., Collins, J. K., … Ferrari, A. J. (2021). Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet, 398(10312), 1700–1712. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02143-7
Van Hout, B., Janssen, M. F., Feng, Y. S., Kohlmann, T., Busschbach, J., Golicki, D., ... & Pickard, A. S. (2012). Interim scoring for the EQ-5D-5L: mapping the EQ-5D-5L to EQ-5D-3L value sets. Value in health, 15(5), 708-715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2012.02.008